Sample Questions
Sample Questions
The questions are constructed based on elementary school Science curricula, reference books and other relevant sources which assess intellectual reasoning and creativity.
Participants are encouraged to read on topics provided in the following syllabus:
| General content | - Science skills and methodology - General health (nutrition, common disease and their prevention) - Current technology development (GMO, biotech, biofuel, satellites etc) |
Biology |
- Basic ecology (habitat, interaction, food chain and food web, population, ecosystem, life cycles) - Physiology (photosynthesis and respiration) - Human anatomy and function (skeleton and movement, olfactory system, auditory system, mouth, eyes, circulatory, digestive system, skin, respiratory system) and some associated diseases and problems - Classifying organisms based on their food, anatomy, reproduction system and habitat - Very common or endangered species names |
Chemistry |
- Properties of Matter - Phase transformations (solid/liquid/gas) - Physical, chemical and biological transformations |
Physics |
- Mechanics (motion of objects, static, fluid, gas) - Electricity and magnetism - Thermal properties (temperature, conduction, convection and radiation) - Light (properties, vision colour) - Forces (magnetic, gravitation, frictional force) - Energy and energy change (kinetic, potential, renewable, energy conversions) |
Earth Science |
- General environmental issue (deforestation, managing natural resource, pollution, water and carbon cycle) - Solar system (rotation of earth and moon, earth and moon eclipses) - The planet earth (structure, surface, climate, seasons, gravitation, wind) |
Sample Questions
The Theory paper consists of 40 multiple choice questions in two Sections: A and B.
Section A comprises 30 questions. For each, four possible answers are provided. Students are to choose the most suitable answer. Each question is worth 1 mark.
Section B comprises 10 questions. For each of the questions, three statements 1 to 3 are provided. One or more of the three numbered statements 3 may be correct.
Students have to decide whether each of the statements is or is not correct.
(They may find it helpful to put a tick against the statement that they consider to be correct.)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 2 and 3 are correct |
1 and 2 only are correct |
2 and 3 only are correct |
1 only is correct |
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
Each question is worth 2 marks. No mark will be deducted for a wrong answer.
Sample Questions for Section A
For each question, four options are given. Only one of them is the correct answer.
Choose the most suitable answer and shade your answer clearly on the Optical Mark Sheet (OMS) provided. Each question carries 1 mark.
1. Which of the following statements describes substances which are gases at room temperature?
A. Their boiling point is below room temperature but their melting point is above.
B. Their boiling point is above room temperature but their melting point is below.
C. Their boiling and melting points are both above room temperature.
D. Their boiling and melting points are both below room temperature.
Answer: D
2. The figure below shows an apparatus set up to investigate the rate of photosynthesis of water weeds.
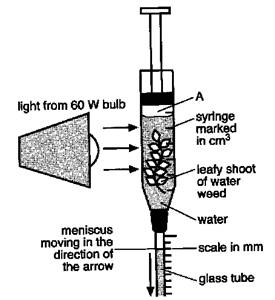
Which of the following will not increase the rate of photosynthesis?
A. Increase in light intensity
B. Increase in temperature to 40 °C
C. Increase in oxygen concentration
D. Increase in concentration of mineral salts in the water
Answer: C
3. In a container, water and ice are found to exist together. What is most likely to be the temperature of the container?
A. Less than 0 degree celcius
B. Around –4 degree celcius
C. 4 oC
D. Exactly 0 degree celcius
Answer: D
4. Coal remains as one of our most precious sources of energy today. Coal contains elements like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and sulfur. The element in coal that gives it the energy content is carbon. Four types of coal were analysed for their composition. The results are given below. Which of the type of coal below gives the highest energy content?
| Type of Coal | Carbon (g) | Hydrogen (g) | Oxygen (g) | Sulfur(s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. | Flame Coal | 4 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.05 |
| B. | Anthracite | 4.8 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.05 |
| C. | Lignite | 6 | 6 | 34 | 0.4 |
| D. | Forge Coal | 9 | 4 | 3 | 0.1 |
Answer: D
Sample Questions for Section B
For each of the questions in this section, one or more of the three numbered statements 1 to 3 may be correct.
Decide whether each of the statements is or is not correct. (You may find it helpful to put a tick against the statement that you consider to be correct.)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 2 and 3 are correct |
1 and 2 only are correct |
2 and 3 only are correct |
1 only is correct |
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
Each question is worth 2 marks. No mark will be deducted for a wrong answer.
1. Which of the following statement(s) is a hypothesis (are hypotheses)?
1. If KMnO4 crystals are heated above the decomposition temperature, 240 oC, they will give off oxygen gas.
2. If pure gold had a density of 0.8 g/cm3, instead of 22 g/cm3, then it would float on water.
3. If iron were as easy to extract from its ores as copper, then its use would have begun much earlier in history.
Answer: D
2. What can we infer when an object floats on water?
1. The object must be less dense than water.
2. The object must be able to float in oil.
3. The object must be submerged with half its volume in water.
Answer: D
3. The diagram below shows the circulatory system in a human body.
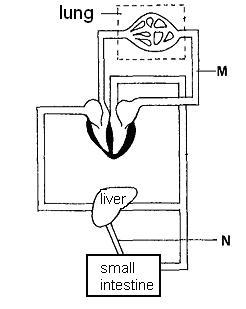
After a lunch meal, what happens to blood vessel M when compared with that of blood vessel N?
1. Blood vessel M carries more oxygen.
2. Blood vessel M carries less carbon dioxide.
3. Blood vessel M carries more digested food.
Answer: B

